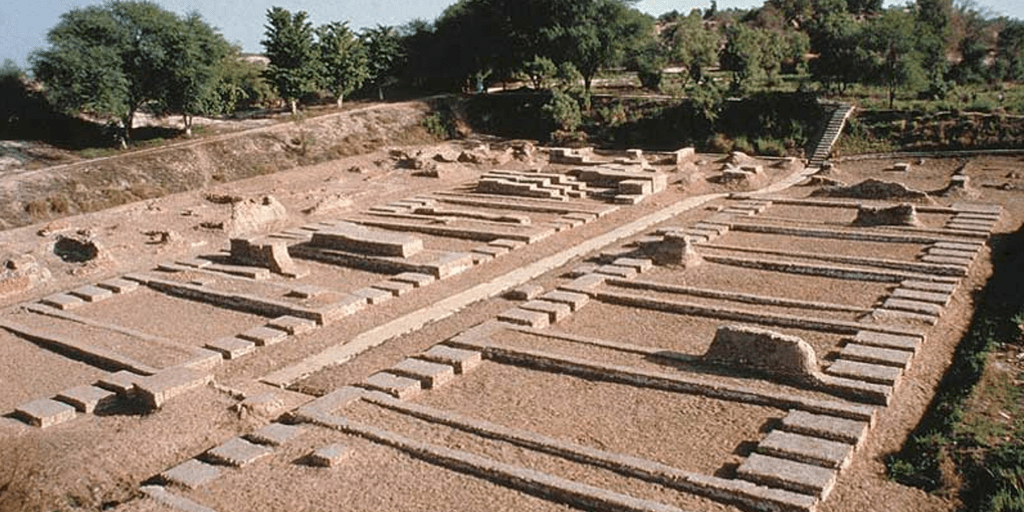
Ancient History of India – A Look to the Harappan (Indus Valley) Civilization

Meaning:
Ancient history belongs to the ancient (old days) time of India. It covers all the aspects or events that were held in the past days in the early ages. Many scholars and intellectuals have discovered so many things from Ancient History. Here we are going to read all such details. The information, pictures, statistics (if any), tabular representation of data (if any) presented here is shown with proper credits.
Ancient History of India is asked in each and every government as well as competitive exams of India. You can either prepare by reading the e-books or can buy the resources from the market. Ancient History covers the complete ancient era. From scratch to details, you will get all sorts of information whatever happened in the past of India. This article is completely dedicated to providing you such details. You can also add your opinion or information in the Comment section below.
Indus Valley Civilization in Ancient History of India
Origin:
The ancient time begins from 2500 BC (approx.) from the origin of Indus Valley Civilization. The civilization started mushrooming on the banks of river Indus. The civilization is popularly known as Harappan Civilization. It was located in the western part of South Asia which today comes under Pakistan and the Western Part of India.
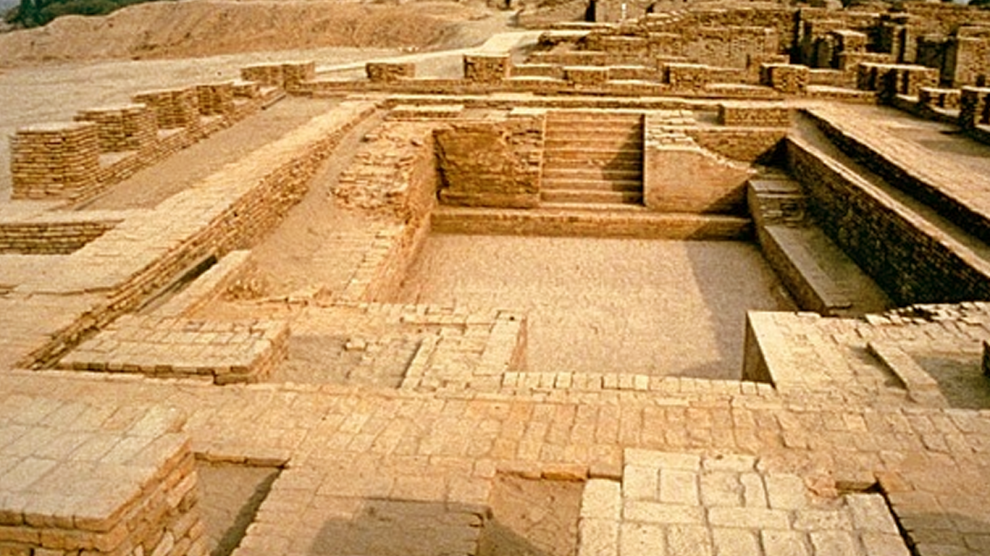

Excavation Done in Ancient India:
Indus Valley or Harappan Civilization was home to the four largest civilizations of Egypt, Mesopotamia, India & China. In the 1920’s Archaeological Department of India carried out an excavation process in the Harappan (Indus Valley) Civilization. In the excavation process, two main and antique cities were excavated which were termed as Mohenjodaro and Harappa itself. Many important and antique figures were unearthed like household articles, weapons, gold & silver ornaments, seals, toys, pottery wares, etc.
After getting all these information and antique items, it was termed as Bronze Age Civilization. This civilization was also known for their development as it is considered as the most urbanized civilization of India.
What Made Ancient India as the Most Urbanized City?
There were baked brick houses, proper drainage systems, water supply systems, clusters of non-residential buildings, new techniques of handicrafts, etc. Along with this, the populations stood at 30,000 to 60,000 individuals which further flourished as 1.5 million individuals.
By the end of 2002, around 1000 mature harappan cities had been reported amongst which only 100 were excavated. After these excavation processes, a total of 5 major urban cities were detected which are Harappa, Mohenjodaro, Dholavira, Ganeriwala in Cholistan and Rakhigarhi.
Phases or Periods in IVC (Indus Valley Civilization):
The cities in the Harappan Civilization had “Social Hierarchies”. It includes their writing patterns, large planned cities, long-distance trade, etc. things marking it a full-fledged civilization. There were periods of this civilization which is categorized below.
The “Mature Phase” of Harappan civilization counted between from C 2600-1900 BCE. There was an inclusion of the predecessor and successor cultures i.e. Early Harappan and Late Harappan. We can understand more about the civilization through this tabular representation:
| Dates | Main Phase | Mehrgarh phases | Harappan phases | Post-Harappan phases | Era |
| 7000–5500 BCE | Pre-Harappan | Mehrgarh I
(aceramic Neolithic) |
Early Food Producing Era | ||
| 5500–3300 BCE | Pre-Harappan/Early Harappan | Mehrgarh II–VI
(ceramic Neolithic) |
Regionalisation Era
c. 4000–2500/2300 BCE (Shaffer) c. 5000–3200 BCE (Coningham & Young) |
||
| 3300–2800 BCE | Early Harappan
c. 3300–2800 BCE (Mughal) c. 5000–2800 BCE (Kenoyer) |
Harappan 1
(Ravi Phase; Hakra Ware) |
|||
| 2800–2600 BCE | Mehrgarh VII | Harappan 2
(Kot Diji Phase, Nausharo I) |
|||
| 2600–2450 BCE | Mature Harappan (Indus Valley Civilisation) | Harappan 3A (Nausharo II) | Integration Era | ||
| 2450–2200 BCE | Harappan 3B | ||||
| 2200–1900 BCE | Harappan 3C | ||||
| 1900–1700 BCE | Late Harappan | Harappan 4 | Cemetery H
Ochre Coloured Pottery |
Localisation Era | |
| 1700–1300 BCE | Harappan 5 | ||||
| 1300–600 BCE | Post-Harappan
Iron Age India |
Painted Grey Ware (1200–600 BCE)
Vedic period (c. 1500–500 BCE) |
Regionalisation
c. 1200–300 BCE (Kenoyer), c. 1500, –600 BCE (Coningham & Young) |
||
| 600–300 BCE | Northern Black Polished Ware (Iron Age) (700–200 BCE) Second urbanisation (c. 500–200 BCE) | Integration |
(Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indus_Valley_Civilisation)
Pre-Harappan Era: Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh is a Neolithic site in the Balochistan province of Pakistan. It was founded in 7000 BCE to C. 2500 BCE). The emergence of this site, gave an extraordinary overview to the emergence of Indus Valley Civilization (IVC). This was founded in South Asia and among the earliest sites known for evidence of farming & herding. This site had grown with domesticated wheat varieties, early phase of farming, pottery and other activities.
Early Harappan Era
The early Harappan phase was located near Ravi River and lasted between C 3300 BCE until 2800 BCE. It is associated with Hakra Phase, which is founded in the Ghaggar-Hakra River Valley, named after a site Sindh in Pakistan near Mohenjodaro. There were popular trade networks which linked this culture to the regional culture.
In this era. People started domesticating crops like peas, sesame seeds, dates and cotton, as well as animals, including the water buffalo. The final stage of this era was recognized by the buildings of large wall settlements, the expansions of trades to other areas, pottery styles, including other regional communities for better trade, ornaments, stamp seals, etc.
Mature Harappan Era
As per the Giosan et al. (2012), the slow progress of the southward monsoons across Asia allowed IVC to develop by taming the floods of the Indus river and its tributaries. The population this time were so intellect that they had utilized the flood water for forming and cultivated large surplus for better living. They did not know the actual farming and became dependent on the seasonal monsoon and floods. By 2600 BCE, the Early harappan civilization changed into large urban cities which included the following:
- Harappa
- Ganeriwala
- Mohen-jodaro
- Dholavira
- Kalibanga
- Rakhigarhi
- Rupar and
- Lothal
In the whole excavation process, total 1000 cities and settlements were found, that too in the main regions of Indus and Ghaggar-Hakra Rivers and their tributaries. So these are some of the information about the excavation and urbanization held in those days at Harappan Civilization. Now moving further, we are going to get knowledge on Technology, Art & Culture, etc. things.
Infrastructure of Indus Valley Civilization:
As we all know that around 2600 BCE, the early harappan civilization started mushrooming. These communities had developed into large urban centers. Amongst all, Mohenjodaro was one of the most sophisticated cities founded. It was developed with advanced engineering and proper town planning methods.
The IVC or Harappan civilization was home to as many as 23,500 residents living in sculpted houses with flat roofs made up of red sand and clay. The city was spreaded into 150 hectares-370 acres and fortified administrative and religious centers of the same kind as found in Mohenjo-daro.
Both cities i.e. Harappa (IVC) and Mohenjo-daro had similar compositions and had citadels, central areas in the city that were heavily fortified-protected with defensive military structures. Additionally, both cities were excavated on the banks of Indus (Sindhu) River.
Some Important Infrastructure Residue of IVC:
- Well ordered waste water drainage
- Trash collection system
- Public baths and granaries, which were storehouses for grains.
- Distinct neighborhoods for artisans and merchants.
- Municipal government.
- Priority on hygiene and religious ritual.
- Dockyards, Granaries, Warehouses.
- Brick platforms, & protective walls.
- Massive for flood protection.
- At Mohenjo-daro, there were great giant baths, public bathing and social areas.
(Source:https://nmk.world/town-planning-system-indus-valley-civilization-harappan-civilization-232/)
Technology & Innovation
The population of Indus Valley (Harappa) Civilization achieved many notable technologies. This includes great authenticity in their systems and tools for measuring length and mass. The architecture involves the following things:
- Fire-baked-bricks (uniform and moisture resistant) utilized in building the great baths & sewage systems.
- Harappa, Mohenjo-daro and recently excavated rakhigarhi are thus known for their urban sanitization process.
Individual homes were drawing from wells and on the other hand, the waste water was going to the covered drains on the main streets of the civilization. Houses were opening in the inner courtyard and smaller lanes. The homes in the outskirts were also connected to the system. Along with this cleanliness is the important matter there. The people of Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) maintained proper hygiene and had clean streets and sitting areas.
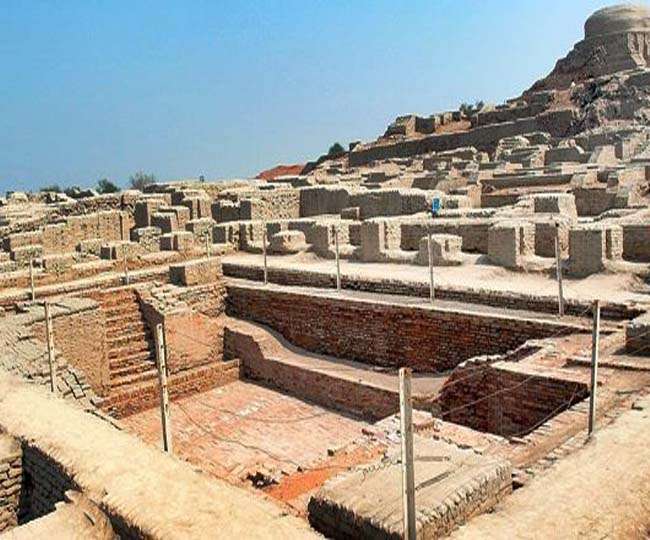

Equipements Utilized:
Harappan civilization was also known for their Seal Carving. They cut patterns into the bottom of the face of the seal, a small, carved object used for stamping. They utilize these seals for the identification of property and to put a stamp on the trade of goods.
Preparation of Seals:
These seals were prepared with animal figures i.e. Elephants, Tigers and Water Buffalos. These seals were utilized differently as per the trading patterns. Simultaneously, the involvement of Metallurgy Technique named this civilization as Bronze Age Society. People at IVC started utilizing Copper, Bronze, Lead, Tin in manufacturing of ornaments, weapons, seals, and other equipment.
Handicrafts & Trade:
People here also did handicrafting using the semi-precious gemstone stone “Carnelian”. These were utilized for trading purposes only. There was evidence that Harappan Civilization participated in the Maritime-Sea-Trade network which was extended from Central Asia to the Middle East.
It was noticed that the complete economy was dependent on Trade business only, which was supported with advanced technology and methods. It was also noticed that IVC was the only civilization to use wheeled transport for trading purposes. They built Oxcarts to carry their trades between other regional communities.
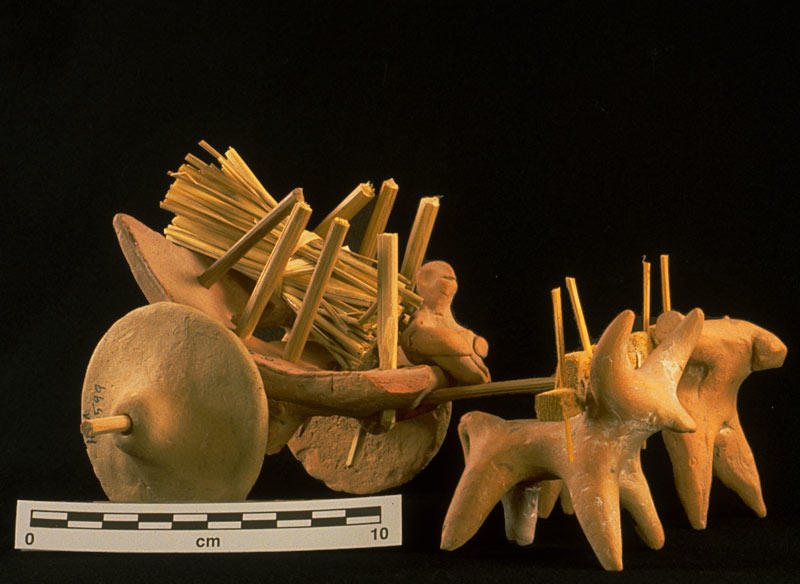

Other Things Which Was Noticed For Trading:
- Boats and Watercraft
- Massive & Dredged Canal
- Docking Facilities at the coastal areas of Lothal City.
- Shellworking was also seen.
- Shells were utilized their craft works
Harappan Civilization’s Region, Language & Culture:
There was not that much evidence of religion, caste, creed and language. A few books or notes, or evidence were found explaining a little about the Harappan Culture. According to the excavation done at Harappa, a text was found over clay and stone tablets which were carbon dated between 3300-3200 BCE.
This was trident shaped, plant-like markings that appeared to be written from right to left. There was a debate to it also that it could be an encoded language and could be related to Indo-European and South Indian families.
Harappan Culture:
There was much speculation about ancient time, especially for Indus Valley Civilization (IVC). It was assumed that they worshiped Goddesses that symbolize Fertility. But there was no such evidence i.e. Temple or Palaces of worship, etc. There were no clear clues of religious rites or specific deities.
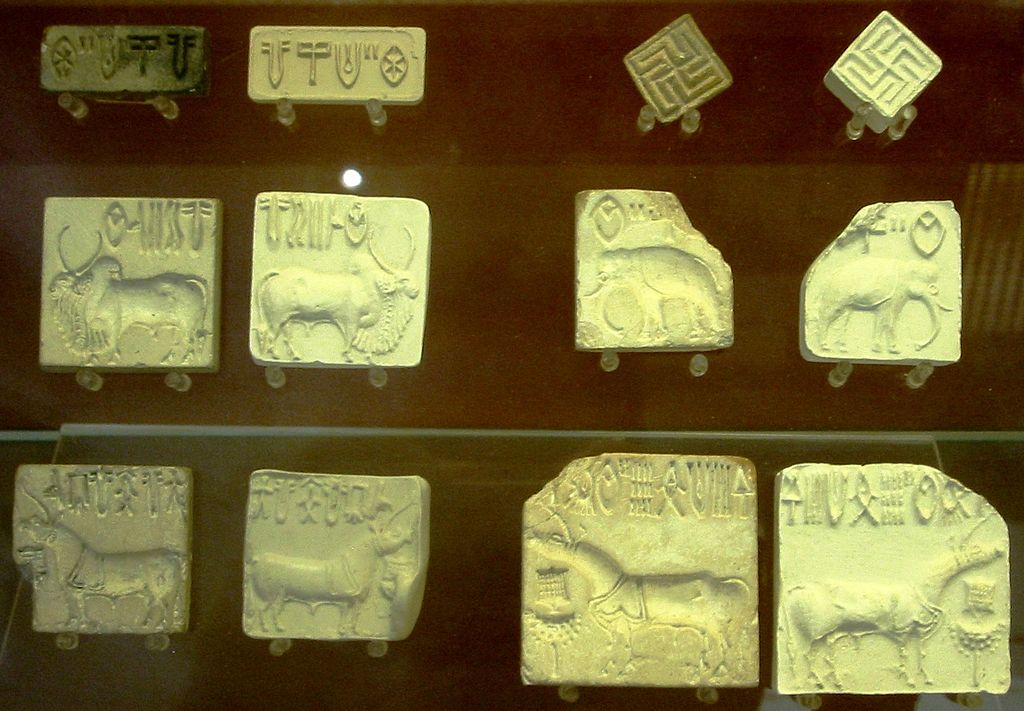

Indus Valley Civilization Culture:
The Harappan (Sindhu) Civilization had shown various examples of Art & Culture work there. In the excavation process, Sculpture, Seals, Pottery, Gold Jewellery & Terracotta, bronze, steatite figures had been found.
The terracotta and gold figures were of King-Priest which had a beard and patterned robe. Another figure was found of a Dancing Girl made up in Bronze. It is only 11 cm high and was in a post of some sort of dancing.This proves that there were sources of entertainment and they followed a very good & systematic culture.
Now, the terracotta work includes utilization of animal images like Cows, Bears, Monkeys and Dogs. Meanwhile in the process, ornaments like Necklaces, Bangles and other jewellery were also found.
How Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) Declined?
The termination or decline of Harappa Civilization was noticed around 1800 BCE. According to some theories, A nomadic, Indo-European civilization “Aryan” invaded the Indus Valley Civilization and conquered all the areas. Similarly, many archaeologists believed that the decline was faced because of bad climatic conditions.
Some of the scholars believed that drying of the Saraswati River led to the decline of Harappa Civilization. It was noticed around 1900 BCE. There were many theories propounded on the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization, among which this was also believed that changes in the river pattern segregated the large civilization into smaller one which was termed as Late Harappa Culture.
Some of the scholars also suggested that IVC climate developed cooler, drier and a tectonic event which had led to the diversion of the river, which was the source of living of IVC people. By around 1700 BCE, most of the Indus Valley (Harappa) Civilization had been abandoned and now the excavation is still on the banks of the Indus River to find more about this largest civilization.

